 For many, a car serves as the primary method of transportation on a daily basis. However, no matter how careful someone is while on the road or how skilled they are at driving, other motorists who do not follow the traffic laws pose a significant threat. When others are careless and cause accidents or even fatalities to occur on the road, those who are responsible can be held accountable for their actions through a Texas personal injury lawsuit.
For many, a car serves as the primary method of transportation on a daily basis. However, no matter how careful someone is while on the road or how skilled they are at driving, other motorists who do not follow the traffic laws pose a significant threat. When others are careless and cause accidents or even fatalities to occur on the road, those who are responsible can be held accountable for their actions through a Texas personal injury lawsuit.
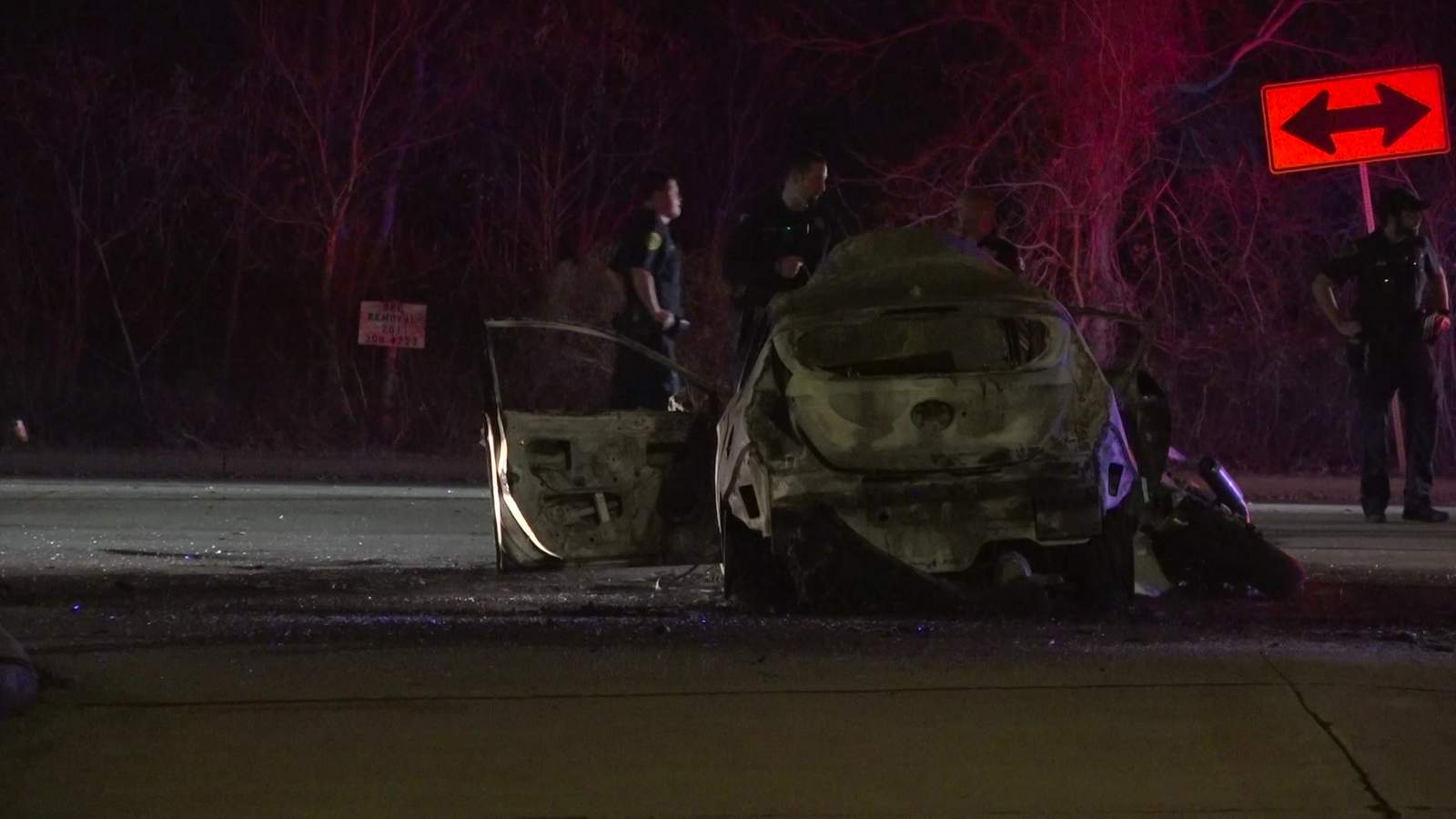
In a recent news report, a young Sheriff’s Deputy and his fiancé were killed in a tragic car accident. Officials say that a tanker truck may have run a stop sign and crashed into the deputy’s vehicle, which killed his fiancé on impact. He passed away shortly after and his brother, who was also a passenger, was airlifted in critical condition to a local hospital with spinal, facial, and arm injuries.
In Texas, cases like these can often pave the way for potential wrongful death claims. To file a wrongful death claim, one must first ensure that the circumstances surrounding their potential case fall within Texas’s definition of wrongful death. Claims can be filed by specific parties if the death is caused by a wrongful act involving carelessness, unskillfulness, or neglect. Thus, potential plaintiffs could have a claim if their loved ones die because of the negligence of others, such as during a major car accident, or a vehicle collision involving distracted driving.
 Texas Injury Lawyers Blog
Texas Injury Lawyers Blog


 We’ve all been distracted while driving at some point while navigating our vehicles. Whether it’s exhaustion from a full day of work causing you to doze off or an urgent phone call out of nowhere from the office, we’ve all had a moment where we’ve zoned out while driving. However, not everyone is fortunate enough to emerge from these situations safe and sound. Often, accidents occur as a result of drifting off or distracted driving, and can have enormous, disastrous impacts. When such accidents occur and tragedy strikes, those who cause them can be held responsible for their actions.
We’ve all been distracted while driving at some point while navigating our vehicles. Whether it’s exhaustion from a full day of work causing you to doze off or an urgent phone call out of nowhere from the office, we’ve all had a moment where we’ve zoned out while driving. However, not everyone is fortunate enough to emerge from these situations safe and sound. Often, accidents occur as a result of drifting off or distracted driving, and can have enormous, disastrous impacts. When such accidents occur and tragedy strikes, those who cause them can be held responsible for their actions. An accident is always inconvenient, and costly, as well as dangerous. If you’re in an accident, it’s important to first call 911 immediately for anyone who is injured. Your next step? Call
An accident is always inconvenient, and costly, as well as dangerous. If you’re in an accident, it’s important to first call 911 immediately for anyone who is injured. Your next step? Call 

